Things about Solvent Recovery - Jacobi Carbons


Tailings Solvent Recovery Units - Oil Sands Magazine

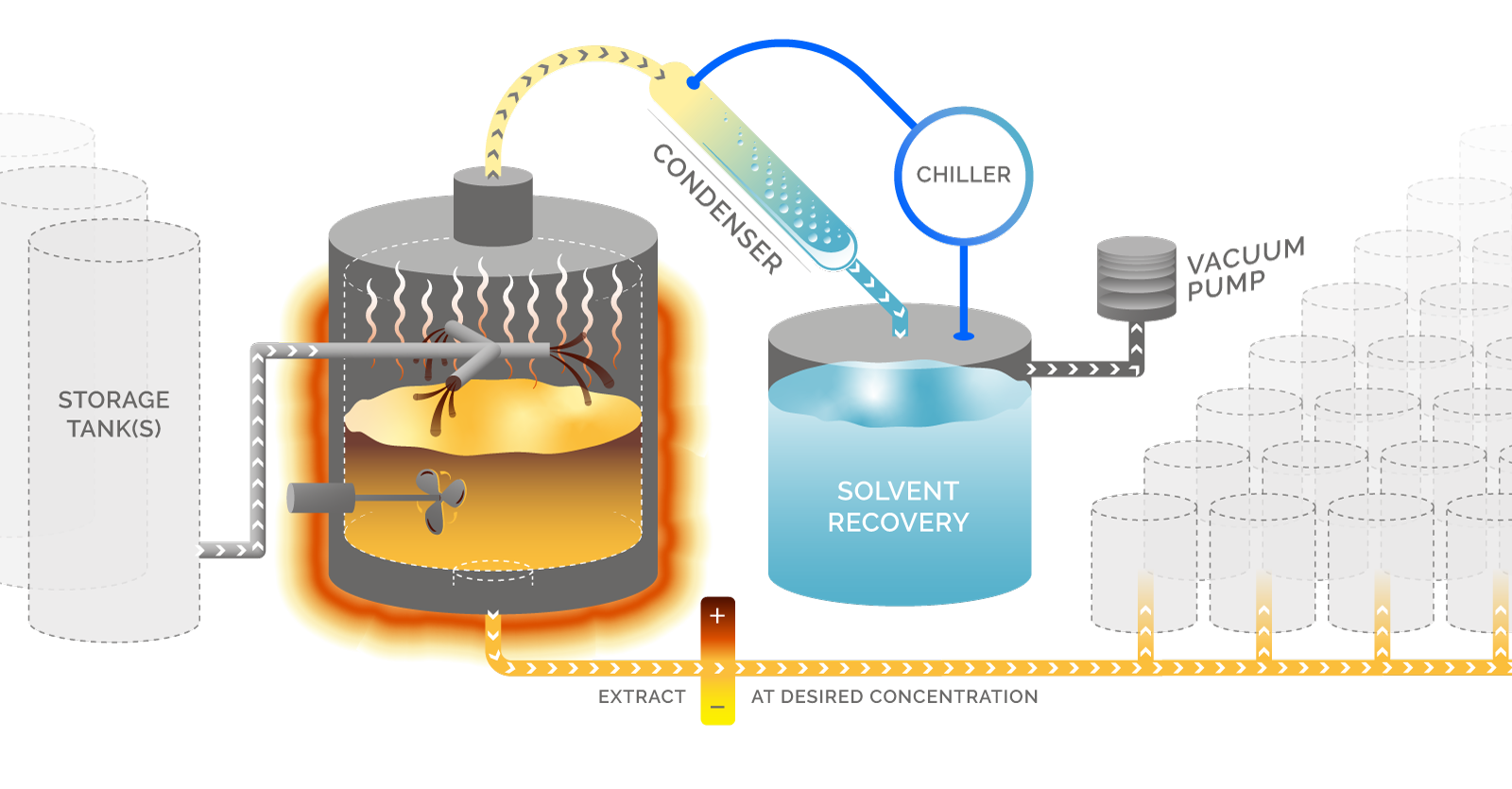
Solvent Recovery Unit ASC-150 - OFRU Recycling
Pharmaceutical concentration using organic solvent forward osmosis for solvent recovery - Nature Communications
CG-1272 - DISTILLATION RECEIVERS, SOLVENT RECOVERY, GRADUATED- Chemglass Life Sciences Things To Know Before You Buy
Numerous solvent applications can recover initial inputs to their complete previous pureness by extracting them entirely from the effluent stream. Recovering 75% of the input volume of a chemical solvent at full purity for reuse is a common outcome of this type of system, and in these cases the recovered solvent should be as reliable as a new solvent. However not all solvents are recoverable to initial state, depending upon how they were used and the relative boiling points of substances in the effluent stream. The composition of reclaimed solvent is really dependent on how well you can separate (and generally how close in boiling point) solvents and other chemicals are.
Adsorptive solvent healing systems have at least 2, however usually 3 or 4 parallel-connected fix-bed adsorbers which pass successively through the four phases of the operation cycle. 1-418-23 Adsorption Desorption Drying Cooling Whilst adsorption happens in one or more of them, desorption, drying and cooling happens in the others. The most typical adsorbent is triggered carbon in the shape of 3 or 4 mm pellets or as granular type with a particle size of 2 to 5 mm (4 x 10 mesh). A schematic flow sheet of a two adsorber system for the removal of water-insoluble solvents is shown in Fig 22.
The adsorber feed is pre-treated if essential to remove Figure 22. 1.4. Circulation sheet of a solvent recovery system with steam solids (dust), liquids (drplets OT desorption. Figure 22. 1.5. Principle of steam desorption. aerosols) or high-boiling components as these can hinder performance. Frequently, Read More Here cooling. To prevent an excessive temperature boost throughout the bed due to the heat of adsorption, inlet solvent concentrations are usually restricted to about 50 g/m3. In many systems the solvent-laden air stream is directed upwards through a fixed carbon bed. As quickly as the optimum allowable development concentration is obtained in the discharge tidy jet stream, the loaded adsorber is changed to regrowth.

